Are you struggling to manage your company’s workflows and processes efficiently? Do your teams lack visibility into how work gets done across departments? Our business process management software guide explains how these systems can solve those problems.
By automating workflows, optimizing processes, and providing insights into operations, BPM software can help your business boost productivity, reduce costs, and improve agility. Read on to learn how to select the right BPM solution for your organization.
Key Takeaways
- Business Process Management (BPM) software streamlines workflows, automates tasks, and provides real-time insights, leading to increased efficiency, cost reduction, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Understanding the different types of BPM software (open-source, on-premise, cloud-based, etc.) and their key features is crucial for selecting the right solution.
- A well-defined strategy, stakeholder involvement, process mapping, and continuous monitoring are essential for successfully implementing and optimizing BPM initiatives.
- BPM can optimize diverse business processes, from accounts payable and sales pipelines to compliance management and product lifecycle management.
- Choosing the right BPM software requires careful evaluation of usability, reporting capabilities, integration, mobility, and cost-effectiveness to align with business needs.
- Mastering BPM involves embracing automation, standardization, employee training, and a culture of continuous improvement to drive operational excellence and competitiveness.
What Is Business Process Management (BPM)?
BPM (Business Process Management) is the practice of creating, analyzing, and optimizing business processes to achieve organizational goals efficiently. It involves identifying, modeling, monitoring, and improving the series of activities and tasks that make up a business process, ensuring it runs smoothly and effectively.
The primary goal of BPM is to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity by eliminating inefficiencies, automating repetitive tasks, and aligning processes with strategic objectives. It encompasses a wide range of methods, tools, and technologies that enable organizations to visualize, document, and optimize their processes.
BPM is an ongoing cycle of continuous improvement, where processes are regularly reviewed and refined to adapt to changing business requirements, customer demands, and market conditions.
By embracing BPM, organizations can gain a competitive edge, and improve customer satisfaction, and achieve operational excellence.
What is Business Process Management (BPM) Software?
BPM Software, short for Business Process Management Software, is like a smart guide for companies to organize their work better. Imagine a tool that helps you line up all the steps for tasks such as welcoming new customers, making plans, getting materials, sending out products, and billing people.
It’s not just about making a list; it’s about finding the smartest, quickest ways to get these things done. This software helps businesses of all sizes in any job area to make their work smoother by finding and fixing slow spots, cutting down costs, and making products and services better.
For instance, it can automatically decide which customer needs a quick response based on their actions, make joining forms for new clients easy and quick, and take care of everyday tasks like gathering information and making reports without people having to do it over and over.
Types of BPM Software
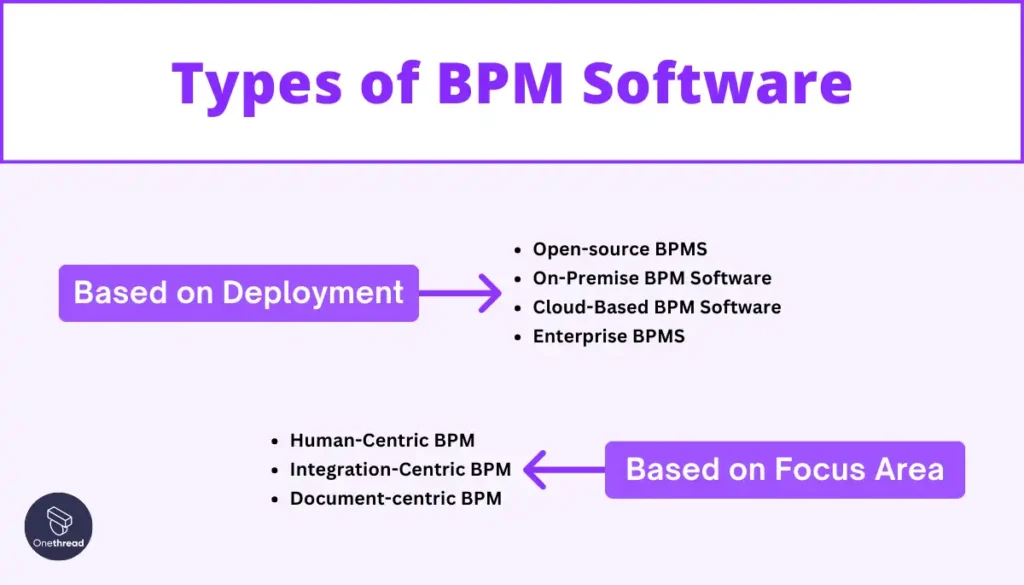
There are different kinds of BPM (Business Process Management) software based on how they’re deployed (open-source, on-premise, cloud-based, enterprise) and what they focus on (human interactions, system integration, document management). Each type caters to specific business needs, so choose wisely.
The deployment model determines where the software runs and who manages it. Open-source BPM is free and customizable but requires technical expertise. On-premise is installed locally, offering full control but higher costs. Cloud-based is hosted remotely, providing flexibility and lower upfront costs. Enterprise solutions are robust and scalable for large organizations.
The focus area defines the software’s primary purpose. Human-centric BPM facilitates collaboration and decision-making involving people. Integration-centric automates processes across different systems. Document-centric manages the entire lifecycle of documents, from creation to approvals.
Understanding these distinctions helps select the right BPM software aligned with your organization’s specific processes and requirements. So, let’s dive in to get the details of each type.
Open-source BPMS
Open-source BPMS (Business Process Management Software) is freely available software that allows businesses to design, model, implement, and optimize their processes. It offers the flexibility to modify the source code to meet specific needs, fostering innovation and customization.
Open-source BPMS encourages collaboration among users and developers, continuously improving the software through community contributions. While it reduces upfront costs, businesses may invest in technical expertise for customization and maintenance.
Ideal for organizations with the capability to tailor their BPM solutions and those looking for cost-effective alternatives, open-source BPMS provides a platform for efficient process management with the added benefit of community support.
On-Premise BPM Software
On-premise BPM (Business Process Management) software is installed and runs on the company’s own servers and infrastructure. It offers full control over the BPM system, including customization, security, and data management.
Businesses can tailor the software to meet specific needs and integrate it seamlessly with existing systems. On-premise BPM provides a higher level of data security, as all information remains within the company’s private network.
However, it requires a significant initial investment in hardware and software, as well as ongoing costs for maintenance and IT staff.
This type of BPM software is ideal for organizations with strict data security requirements and those willing to invest in a robust, customizable system.
Cloud-Based BPM Software
Cloud-based BPM (Business Process Management) software is hosted on the provider’s servers and accessed via the Internet. It offers flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on demand.
This type of BPM software reduces the need for a large initial investment in hardware and IT infrastructure. It provides easy access from anywhere, facilitating remote work and collaboration.
Cloud-based BPM ensures that software updates and maintenance are handled by the provider, ensuring the system is always up-to-date. Ideal for businesses looking for cost-effective solutions and those that prioritize flexibility and ease of access.
Enterprise BPMS
Enterprise BPMS (Business Process Management Suites) are comprehensive solutions designed to serve large organizations with complex operational needs. These suites offer a wide range of features, including process modeling, automation, execution, monitoring, and optimization tools.
They are built to integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise applications, facilitating data exchange and streamlining workflows across the organization. Enterprise BPMS supports collaboration among multiple departments, enabling more efficient decision-making and process improvements.
Ideal for large-scale businesses seeking to optimize their entire operation, these solutions provide the robustness, scalability, and customization capabilities necessary to manage complex, enterprise-wide processes efficiently.
Human-Centric BPM
Human-centric BPM software is built around activities that require human interaction, such as approvals and decision-making. This type of BPM emphasizes improving collaboration and communication among team members.
It provides tools for assigning tasks, pausing them, and tracking progress with a user-friendly interface. Human-centric BPM is great for processes that cannot be fully automated and rely on human intelligence and decision-making skills.
Integration-Centric BPM
Integration-centric BPM software is designed to connect different software systems, like CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), and HRMS (Human Resource Management System).
It’s perfect for processes that require minimal human intervention. This type uses APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and connectors to speed up process flows, making it ideal for businesses looking to automate and integrate their various software systems seamlessly.
Document-centric BPM
Document-centric BPM software is essential for businesses where documents, such as contracts or reports, play a central role in their processes.
This type focuses on managing the lifecycle of documents – from creation and formatting to verification, routing, and signing. It’s designed to ensure that documents move smoothly between teams and processes, making it a critical tool for industries like law, engineering, and contract management.
Why Your Business Needs BPM Software

Business Process Management (BPM) Software is essential for modern organizations aiming to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance. By automating, monitoring, and optimizing business processes, BPM software brings numerous benefits, from increased efficiency to improved customer satisfaction.
Understanding why your business needs BPM software can be the key to unlocking sustainable success and staying competitive in today’s fast-paced market.
Increased Efficiency
BPM software automates routine tasks and streamlines workflows, significantly reducing processing times and eliminating unnecessary steps.
For example, a retail business can use BPM to manage its inventory more effectively, using sensors and real-time data to maintain optimal stock levels.
This not only prevents stockouts and overstocking but also allows employees to concentrate on more value-added activities, boosting overall efficiency.
Cost Reduction
In the competitive business landscape, cutting costs without compromising quality is crucial. BPM software helps identify inefficiencies and areas where expenses can be reduced.
A manufacturing company, for instance, can use BPM to optimize its procurement process, selecting efficient suppliers and negotiating better prices based on historical data, leading to significant cost savings.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Delivering products and services faster and more accurately enhances customer satisfaction. BPM software enables businesses to streamline customer-facing processes, ensuring a smoother, more reliable experience. This can lead to repeat business and a stronger brand reputation.
Increased Agility
BPM software allows businesses to quickly adapt to market changes and emerging trends. By automating processes like loan approvals, financial services companies can make faster decisions, helping them stay ahead of competitors and meet customer needs more effectively.
Enhanced Visibility
With BPM software, companies gain real-time insights into their operations, helping identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. This visibility enables timely corrective actions, ensuring processes run smoothly and efficiently.
Better Compliance
BPM software ensures processes are in line with regulations and standards, helping avoid fines and legal issues. It automates compliance tasks, like monitoring payments for adherence to Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS), safeguarding against breaches and non-compliance.
Standardization
BPM software helps standardize processes across all locations, ensuring consistent quality and performance. This is crucial for businesses looking to maintain high standards and uniformity in their products and services.
Employee Empowerment
Providing employees with the tools and information they need through BPM software boosts motivation and productivity. It enhances decision-making and allows for more effective responses to customer inquiries and issues.
Innovation
BPM software supports innovation by offering insights and data that can inform new strategies and process improvements. This continuous innovation keeps companies competitive and can lead to revenue growth.
Competitive Advantage
BPM software gives businesses the agility, efficiency, and customer focus needed to outperform rivals. It enables the optimization of core processes, leading to reduced costs, improved delivery times, and better customer experiences.
Implementing BPM software can transform your business, making it more efficient, agile, and customer-centric. It’s an investment in future-proofing your organization and ensuring its growth and sustainability in the digital age.
Key Features of BPM Software
BPM (Business Process Management) software streamlines operations, enhances efficiency and drives digital transformation. It equips organizations with tools for designing, implementing, analyzing, and improving business processes.
Knowing the key features of BPM software can help businesses select the right platform that aligns with their goals and requirements. Below are essential features categorized under Master Features and Design Features.
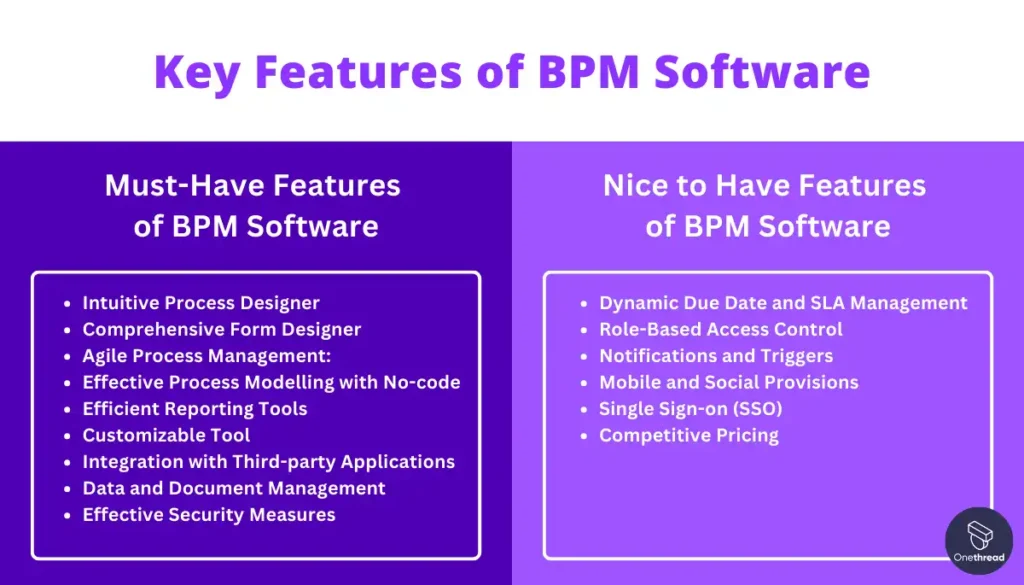
Must-Have Features of BPM Software:
- Intuitive Process Designer: Enables easy creation and modification of business processes through a user-friendly drag-and-drop interface. It requires no coding skills, allowing users of all levels to design workflows and processes effectively.
- Comprehensive Form Designer: Offers a robust drag-and-drop tool for creating forms that are the foundation of business processes. Supports sophisticated layouts and multiple field options, ensuring forms are easily accessible and mobile-responsive.
- Agile Process Management: Provides flexibility to modify processes in response to changing business environments. It supports quick adjustments, reviews, and process transitions, essential for maintaining process efficiency.
- Effective Process Modelling with No-code: Simplifies the customization of business processes, allowing users to create apps, forms, and workflows without coding knowledge. Enhances rapid deployment and iteration of processes.
- Efficient Reporting Tools: Facilitates the creation of detailed reports and graphs for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and process efficiencies. Includes built-in tools for real-time data analysis, helping businesses make informed decisions.
- Customizable Tool: Ensures the software can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a business. Allows customization at every step of the process flow, enhancing the relevance and effectiveness of the BPM platform.
- Integration with Third-party Applications: Supports seamless integration with existing business systems, enhancing data flow and employee productivity. Essential for a holistic approach to process management.
- Data and Document Management: Manages vast amounts of data and documents, ensuring they are properly organized and accessible. Supports a comprehensive repository for easy access and management.
- Effective Security Measures: Implement stringent security protocols to protect sensitive data and processes from unauthorized access and breaches. Compliance with industry-standard certifications is crucial.
Nice to Have Features of BPM Software:
- Dynamic Due Date and SLA Management: Automates the assignment of due dates based on specific variables, facilitating better management of timelines and service level agreements (SLAs).
- Role-Based Access Control: Ensures sensitive information is accessible only to authorized users, based on their roles within the organization. Enhances data security and integrity.
- Notifications and Triggers: Sends automated alerts and notifications based on predefined conditions, keeping users informed about task progress and important updates.
- Mobile and Social Provisions: Offers mobile access and integrates with social platforms, ensuring users can engage with the BPM software anytime, anywhere, fostering greater collaboration and accessibility.
- Single Sign-on (SSO): Simplifies the login process across multiple platforms, enhancing user convenience and security. Important for organizations using a variety of software tools.
- Competitive Pricing: Provides scalable pricing models that accommodate the growing needs of businesses without significantly increasing costs. Ensures value for money and supports long-term scalability.
Understanding these key features of BPM software will help businesses identify the most suitable platform that caters to their specific process management needs, driving efficiency and innovation.
How to Choose the Right BPM Software

Selecting the right Business Process Management (BPM) software is critical for optimizing your organization’s operations and achieving strategic goals.
Consideration of specific factors ensures you pick a solution that aligns with your business needs, supports your workflows, and enhances overall efficiency.
Step 1: Identify the Problem Statement
Understand the specific challenges or needs your organization aims to address with BPM software. Whether it’s streamlining operations, improving efficiency, or integrating existing systems, clearly defining your problem statement guides you toward a software solution with the necessary features to meet those needs.
Step 2: Assess Usability
Consider the ease of use of the BPM software. It should offer an intuitive user interface that requires minimal training, making it accessible to all users regardless of their technical proficiency. User-friendly software enhances adoption rates and reduces the frustration associated with complex systems.
Step 3: Evaluate Analysis and Reporting Capabilities
Choose BPM software that provides robust analysis and reporting tools. It should allow for the easy generation of reports based on key performance indicators, helping you make informed decisions, identify inefficiencies, and highlight areas for improvement.
Step 4: Consider People, Governance, and Support
Ensure the software supports both the end-users and the management team effectively. Look for features like audit trails, version control, and comprehensive technical support to facilitate clear oversight and accountability across all levels of your organization.
Step 5: Check Content Management and Collaboration Features
Select BPM software that fosters collaboration among teams and facilitates efficient content management. The tool should encourage active use, improve team productivity, and support the exchange of ideas and feedback to drive business success.
Step 6: Analyze Technology and Flexibility
Opt for scalable and flexible BPM software to accommodate future business growth and changing needs. No-code and low-code platforms can be particularly beneficial, offering rapid customization without the need for extensive technical expertise.
Step 7: Review Cost and ROI
While cost is an important consideration, focus on the software’s return on investment (ROI). Evaluate the long-term benefits and savings it can bring to your organization, rather than just the initial purchase price.
Step 8: Inspect Integration Capabilities
The BPM software should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems to unify operations and enhance workflow automation. Look for solutions that support easy integration through APIs, web hooks, and other technologies.
Step 9: Prioritize Mobility
In today’s remote working environment, choose BPM software that is accessible from anywhere, on any device. Mobile optimization is crucial for supporting a flexible and distributed workforce.
Step 10: Decide on Hosting Options
Consider whether on-premise or cloud hosting best suits your organization’s needs. Cloud-based solutions typically offer greater scalability and cost-effectiveness, along with robust security measures.
Step 11: Demand After-Sales Support
Ensure the BPM software provider offers excellent after-sales support, including technical assistance and customer service. Prompt and effective support is essential for resolving any issues quickly and minimizing disruptions to your operations.
Selecting the right BPM software requires careful consideration of these factors to ensure the solution meets your business needs, supports your processes, and delivers tangible improvements in efficiency and productivity.
The 10 Best Business Process Management Tools in 2024
Every year, more and more BPM tools come onto the market. How are you meant to make sense of these complex enterprise-grade applications? Well, we’ve had a lot of conversations about the BPM suites that you can investigate right now. So, look at these brands: maybe one is right for you.
1. Onethread
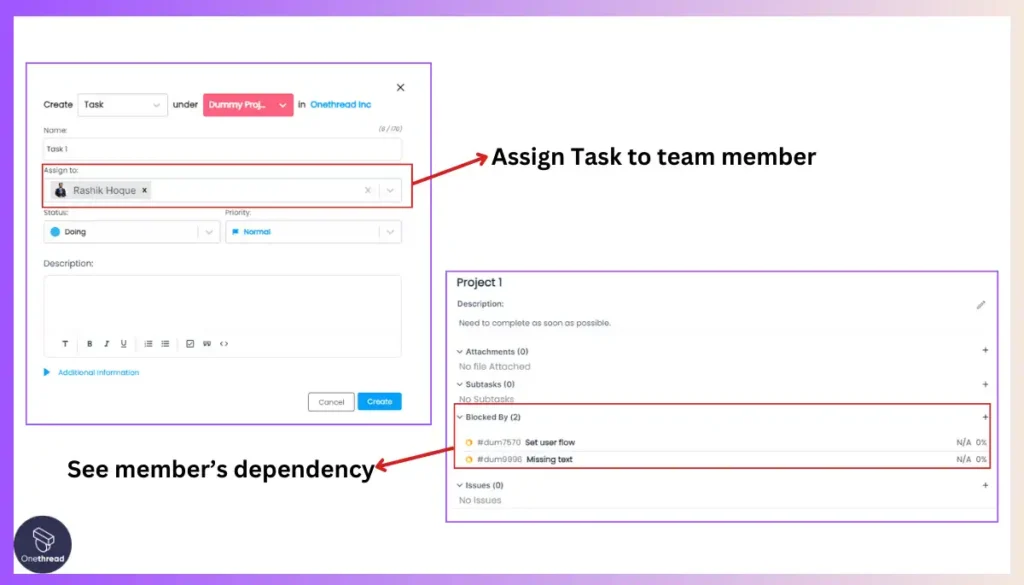
Onethread is a cloud-based project management and collaboration platform that serves as a capable Business Process Management (BPM) solution, tailored for small businesses, startups, and teams. While not an enterprise-level BPM suite, Onethread offers several key BPM features.
Its intuitive process designer allows for building custom workflows, while the “Project Workflows” feature enables automating processes with review, approval, and trigger capabilities.
Onethread provides due-date management for tasks, efficient reporting for monitoring KPIs, and centralized document management with 15GB of storage. It offers mobile apps for iOS and Android, ensuring accessibility. Notifications keep users informed about tasks, approvals, and workflow updates. It also offers setting permissions for specific roles enhancing data security.
However, Onethread may have limitations in advanced integrations with third-party systems commonly found in enterprise BPM suites. Its BPM capabilities are optimized for streamlining operations in smaller organizations rather than handling highly complex, large-scale processes.
Overall, Onethread presents a user-friendly, cloud-based BPM solution suitable for small businesses and teams seeking process optimization, efficient collaboration, and mobile accessibility, while offering essential BPM features like workflow automation, reporting, and document management.
[INSERT_ELEMENTOR id=”12410″]
2. Kissflow
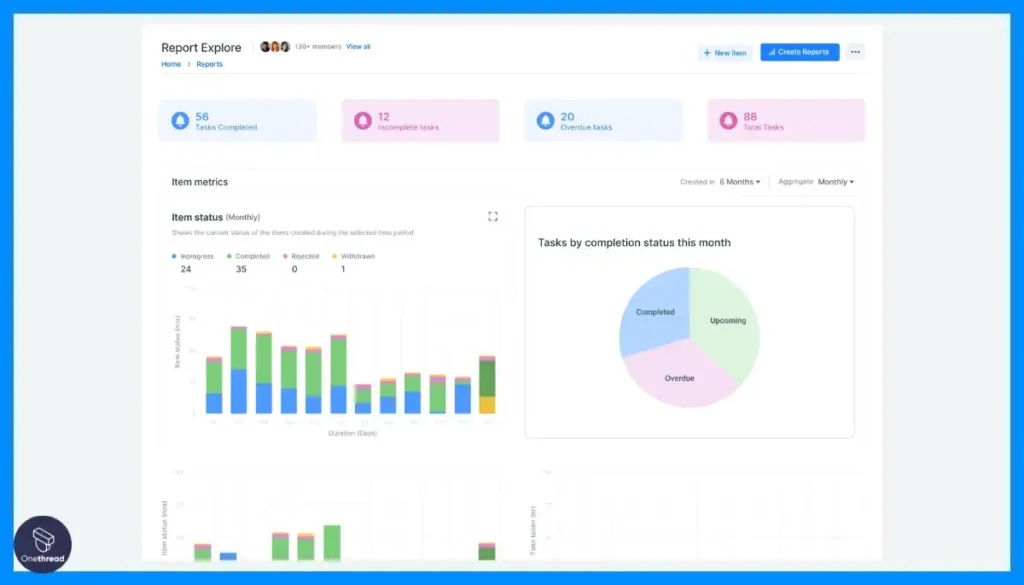
Kissflow offers a drag-and-drop process designer, real-time analytics, mobile apps, and integration with various apps. It provides advanced features like multi-level approval workflows, conditional logic, and process optimization tools.
3. Nintex
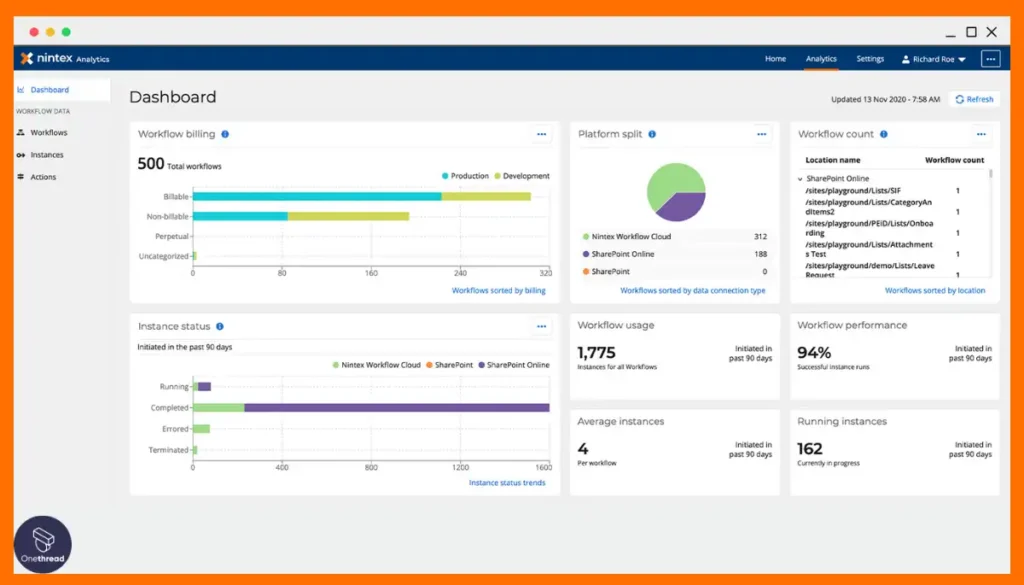
Nintex enables process automation across multiple environments like desktop, mobile, cloud, and on-premises. Its features include drag-and-drop workflow design, forms, mobile apps, document generation, and robotic process automation.
4. Appian
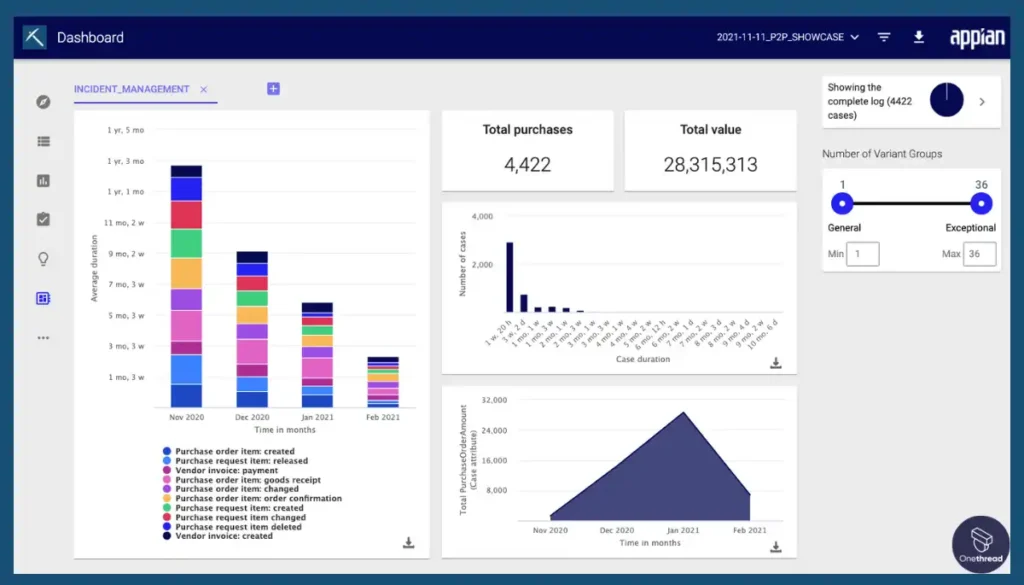
Appian combines low-code development, process management, and case management in a unified platform. It offers features like process modeling, automation, intelligent data capture, and seamless integrations.
5. Bizagi
Bizagi provides process automation, low-code application development, and digital transformation capabilities. Its features include process modeling, automation, analytics, and collaboration tools for process improvement.
6. Process Street
Process Street focuses on creating, tracking, and optimizing recurring processes and workflows. It offers features like checklist templates, stop tasks, role assignments, and conditional logic.
7. Pipefy
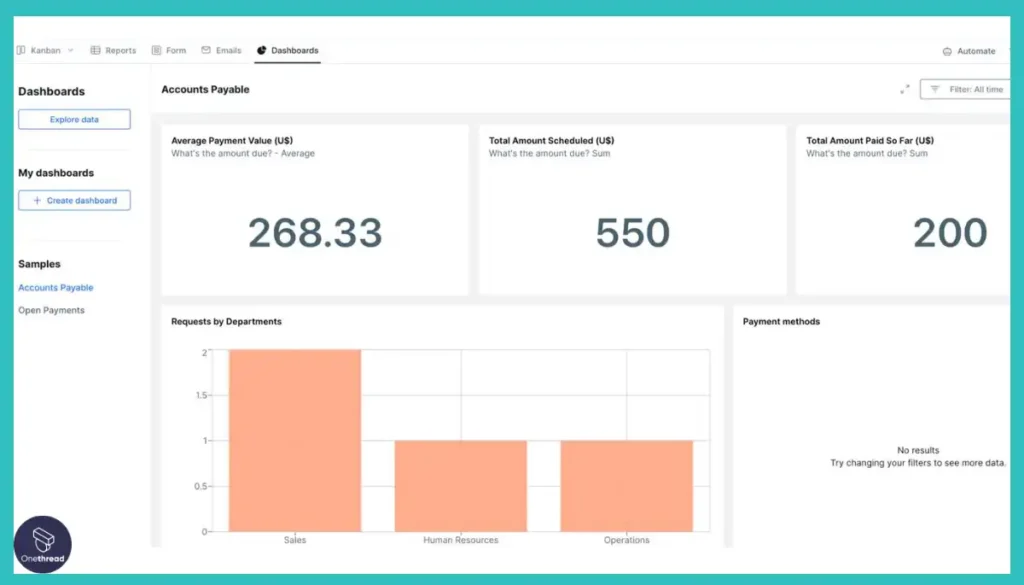
Pipefy is a workflow management tool that enables process automation, collaboration, and visualization. Its features include customizable pipelines, dashboards, integrations, and mobile apps.
8. ProcessMaker
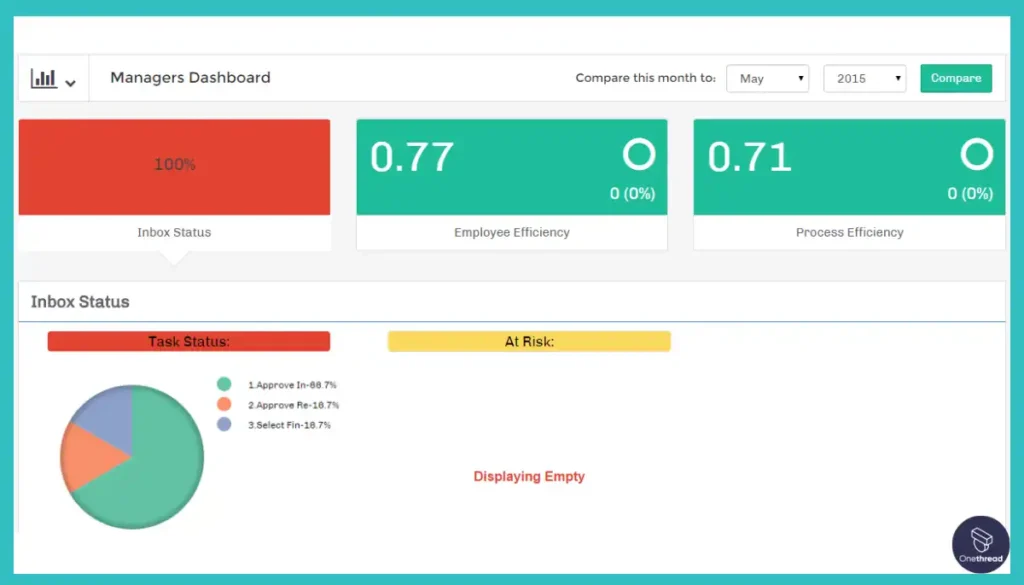
ProcessMaker offers process automation, case management, and low-code application development capabilities. Its features include process modeling, automation, data integrations, and reporting tools.
9. Creatio
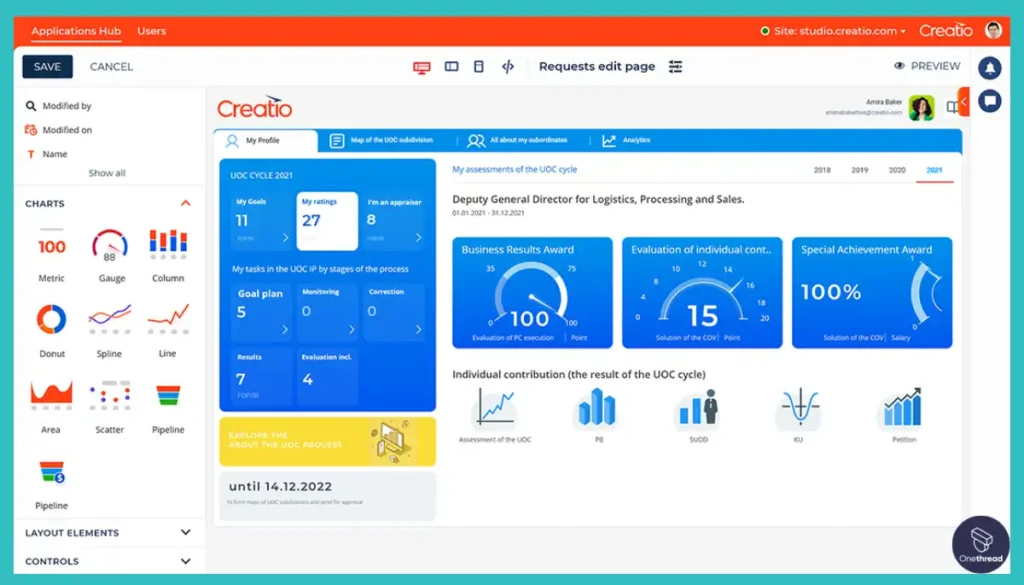
Creatio is a low-code platform for process management, CRM, and enterprise marketing. It offers features like process modeling, automation, case management, and AI-powered analytics.
10. Zoho Corporation
Zoho Corporation provides a suite of business tools, including Zoho Creator for process automation and application development. It offers drag-and-drop tools, integrations, and mobile apps.
Step-By-Step Guide to Business Process Management
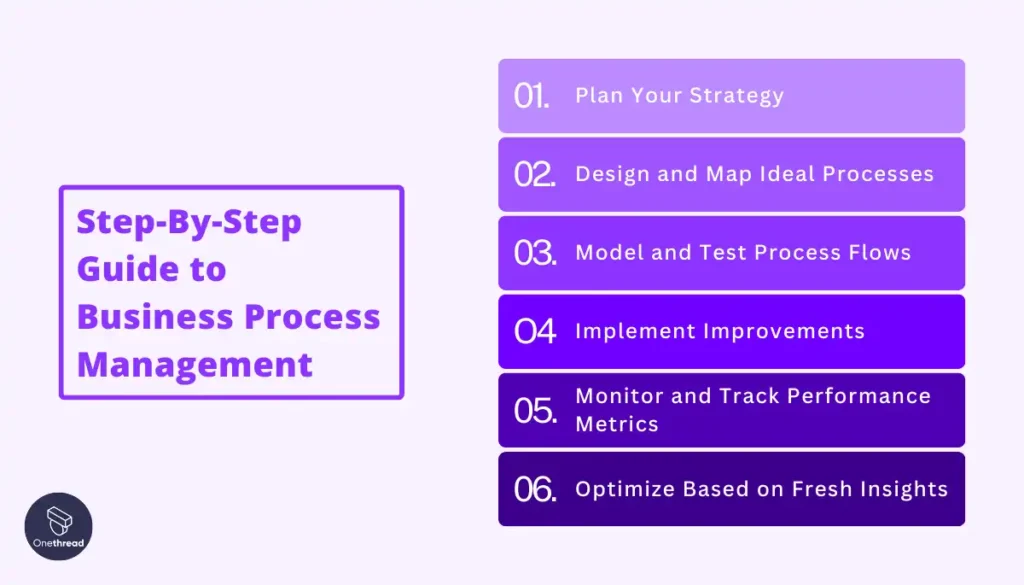
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach organizations use to make their workflow more efficient, effective, and adaptable to an ever-changing environment.
A well-defined BPM initiative can help ensure that any changes to processes bring about the right outcomes. The BPM lifecycle consists of six stages: plan, design, model, implement, monitor, and optimize. Each step plays a crucial role in helping businesses achieve continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Plan Your Strategy
Planning involves collaborating with management to align the BPM strategy with the organization’s core goals. Identify areas for improvement by evaluating current processes and how they contribute to meeting business objectives.
This step is crucial for prioritizing high-impact, low-risk tasks and projects that offer measurable benefits closely aligned with key performance indicators (KPIs).
Design and Map Ideal Processes
After defining strategic objectives, analyze and map each targeted process. Identify bottlenecks, redundant tasks, and areas of excessive costs or errors. Using insights from the “as-is” analysis, design an “ideal” state that addresses these issues. Engage stakeholders to gather data and feedback, ensuring the new design meets business requirements and improves process efficiency.
Model and Test Process Flows
Modeling involves creating a digital representation of the redesigned process, including all tasks, business rules, and data flows. Test this model under various conditions to identify the optimal configuration.
Simulation modeling helps adjust the process design before implementation, ensuring it can achieve desired outcomes without unnecessary costs or delays.
Implement Improvements
Transition to the optimized process by starting with a proof-of-concept or pilot group. Use feedback to refine the process further before a full-scale rollout.
Employ BPM software tools for developing user interfaces and integrating processes, ensuring smooth adoption across the organization. Prepare for change management to support this transition.
Monitor and Track Performance Metrics
Monitor the new process to identify areas for further improvement, using performance metrics aligned with your objectives.
Leverage business intelligence tools to analyze data and generate reports. Regular monitoring helps ensure the process continues to meet its goals and supports the organization’s broader objectives.
Optimize Based on Fresh Insights
Use the data collected during the monitoring phase to refine and enhance the process continually. Look for additional opportunities for automation, standardization, and integration.
The BPM lifecycle is cyclical; as business needs and external conditions change, the process anew to ensure ongoing optimization and alignment with strategic goals.
This step-by-step guide provides a framework for implementing BPM in any organization, ensuring a structured approach to continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Strategies To Master Business Process Management (BPM)

To excel in Business Process Management (BPM), adopting specific strategies is crucial. These strategies ensure that BPM efforts align with your organization’s goals, enhance efficiency, and foster continuous improvement. Here’s how you can master BPM:
Clarify Goals and Objectives
Start by clearly defining what you aim to achieve with BPM. Whether it’s reducing costs, enhancing efficiency, or improving customer satisfaction, having clear goals ensures your BPM initiatives are purpose-driven and aligned with your overall business strategy.
This clarity guides the BPM process, helping to focus efforts on activities that offer the most significant impact.
Involve Stakeholders
Engaging key stakeholders early in the BPM process is vital for gaining their support and ensuring the successful design and implementation of business processes.
Stakeholder involvement helps in understanding different perspectives, addressing concerns, and ensuring that the process improvements meet the actual needs of the organization.
Map Out Current Processes
Documenting and analyzing current processes is the foundation of effective BPM. Utilize workflow diagrams and other tools to visualize processes, identify inefficiencies, and pinpoint bottlenecks.
This step provides a clear understanding of the “as-is” state, which is crucial for planning meaningful improvements.
Standardize Processes
Standardization minimizes errors and streamlines onboarding. Create templates, checklists, and approval workflows to ensure processes are consistent and efficient.
This uniformity also facilitates easier training and quicker adaptation for new employees, contributing to overall organizational agility.
Embrace Automation Technology
Leverage automation tools for repetitive tasks to free up human resources for more strategic work. Automation not only streamlines operations but also reduces the likelihood of errors, enhancing overall process efficiency and effectiveness.
Start Small and Scale
Initiate BPM with less complex processes for easier management and effective implementation. This approach allows for learning and adjustments before scaling up to more significant, organization-wide processes, ensuring smoother transitions and higher success rates.
Invest in Training
Ensure employees have the necessary training to navigate new processes comfortably. Adequate support and change management strategies are crucial for a smooth transition, helping to minimize resistance and foster a positive attitude toward change.
Track Process Performance
Continuously monitor and measure the performance of implemented processes against predefined KPIs. This ongoing evaluation helps identify areas for further improvement and ensures that BPM initiatives remain aligned with organizational goals.
Establish a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Promote a mindset of ongoing enhancement throughout the organization. BPM is not a one-time project but a continuous cycle of evaluating, implementing, and refining processes. Cultivating this culture ensures your organization remains adaptable and competitive.
Mastering BPM requires a structured approach, starting with clear goals and engaging stakeholders through to implementation and continuous improvement.
By following these strategies, organizations can ensure their BPM efforts are effective, sustainable, and aligned with their overarching business objectives.
Business Process Management Examples
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to making an organization’s workflow more effective, more efficient, and more capable of adapting to an ever-changing environment. Here are examples of how BPM can optimize various business processes:
Accounts Payable
BPM streamlines the accounts payable process, ensuring payments are made accurately and on time. For more efficient accounts payable, consider using an invoice template example to streamline invoice processing and ensure timely supplier payments.
By automating invoice processing and payments, organizations can improve cash flow management, reduce errors, and maintain good supplier relationships.
This process directly impacts the financial health of a business, making it essential for consistent, efficient, and error-free operations.
Sales Pipeline
Sales CRM processes are critical for generating revenue and delivering value to customers.
BPM optimizes the sales pipeline by managing leads, tracking customer interactions, and ensuring timely follow-ups. This not only prevents potential sales from slipping through the cracks but also enhances the customer experience and boosts brand reputation.
Customer Support Process
BPM enhances the customer support experience by streamlining service request handling, ensuring timely responses, and tracking resolution progress.
Effective management of customer support processes builds brand loyalty, improves customer satisfaction, and supports a superior customer experience.
HR Processes
HR processes, including employee onboarding and request management, involve multiple departments and systems.
BPM facilitates these complex processes by automating task assignments, streamlining documentation, and ensuring compliance with company policies. This not only enhances the employee experience but also improves operational efficiency within the HR department.
Compliance Management
Compliance management benefits greatly from BPM by ensuring all regulatory requirements are met systematically. BPM tools provide audit trails, manage documentation, and ensure that every step of a process complies with legal and regulatory standards, thereby minimizing the risk of penalties and enhancing organizational credibility.
Loan Origination
For financial institutions, BPM automates and accelerates the loan origination process. By incorporating business rules for credit scoring and eligibility, BPM ensures risk management while improving customer satisfaction with faster loan processing times.
Vendor Management
BPM optimizes vendor management by tracking performance evaluations, managing contracts, and assessing risks efficiently. This ensures that vendor relationships are managed effectively, contributing to the smooth operation of the supply chain and procurement processes.
Approvals Management
BPM streamlines the approval process by setting rules for automatic approvals or rejections based on specific criteria. This reduces manual intervention, speeds up decision-making, and improves overall process efficiency.
Product Lifecycle Management
In manufacturing, BPM streamlines the entire product lifecycle, from concept to distribution. By integrating processes and data, BPM ensures quality control, facilitates communication with suppliers, and manages changes effectively, ensuring products meet market demands efficiently.
Logistics Management
BPM improves logistics by automating order processing and fulfillment tasks, enhancing warehouse operations, and ensuring compliance with customs regulations. This leads to more accurate and timely deliveries, improving customer satisfaction.
Procurement Management
BPM simplifies procurement by automating vendor selection, contract management, and compliance with procurement policies. This leads to more strategic vendor relationships and efficient procurement cycles.
Quality Assurance Management
Quality assurance processes benefit from BPM through integrated quality checks and continuous monitoring. This ensures products and services meet predefined standards, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
By applying BPM to these diverse areas, organizations can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability, driving better business outcomes and enhancing competitiveness in their respective markets.
FAQs
How does BPM software help businesses?
BPM software helps businesses by automating workflows, optimizing processes, and providing insights into operations. This leads to increased efficiency, cost reduction, improved customer satisfaction, increased agility, enhanced visibility, better compliance, standardization, employee empowerment, innovation, and competitive advantage.
What are the key features of BPM software?
The key features of BPM software include an intuitive process designer, comprehensive form designer, agile process management, no-code process modeling, efficient reporting tools, customizability, integration with third-party applications, data and document management, and effective security measures.
What are the different types of BPM software?
The different types of BPM software include open-source, on-premise, cloud-based, enterprise, human-centric, integration-centric, and document-centric BPM software, each catering to specific business needs and deployment requirements.
What are the steps in the BPM lifecycle?
The steps in the BPM lifecycle are to plan your strategy, design and map ideal processes, model and test process flows, implement improvements, monitor and track performance metrics, and optimize based on fresh insights.
What is the difference between human-centric and integration-centric BPM software?
Human-centric BPM software is built around activities that require human interaction, such as approvals and decision-making, while integration-centric BPM software is designed to connect different software systems, such as CRM, ERP, and HRMS, with minimal human intervention.
Bottom Line
Business Process Management (BPM) software is a vital tool for organizations looking to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. By automating workflows, optimizing processes, and offering critical insights, BPM software supports businesses in navigating the complexities of modern operations.
Choosing the right BPM solution tailored to your specific needs is crucial for unlocking sustainable success and maintaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
