Becoming a project manager is an enticing career path offering diverse opportunities across industries. A project manager is a professional responsible for planning, executing, and closing projects, leading teams to achieve objectives within time and budget constraints.
To become a project manager, you can pursue a degree in a relevant field or gain practical experience through alternative education routes like online courses and certifications.
Key skills required include project management methodologies, budgeting, risk assessment, scheduling, leadership, communication, and problem-solving.
This comprehensive guide covers step-by-step approaches for both degree and non-degree pathways, along with essential information on industry-specific requirements, certifications, salary ranges, and job outlooks.
Key Takeaways:
- A project manager is a professional who plans, executes, and closes projects, leading teams to achieve objectives within time and budget constraints.
- You don’t necessarily need a degree to become a project manager; practical experience and certifications can also pave the way.
- Essential skills for PM include project management methodologies, budgeting, risk assessment, scheduling, leadership, communication, and problem-solving.
- The path to becoming a project manager involves a combination of education, certifications, practical experience, and continuous learning and development.
- Project management offers diverse opportunities across industries like construction, IT, tech, and healthcare, each with its own unique challenges and requirements.
- The demand for skilled project managers is projected to grow, making it a promising career choice with lucrative earning potential.
- To streamline your journey and enhance project management proficiency, leverage Onethread, a comprehensive platform tailored for startups, small businesses, and agile teams.
Try Onethread
Experience Onethread full potential, with all its features unlocked. Sign up now to start your 14-day free trial!
Who Is a Project Manager?
A project manager is a professional responsible for planning, executing, and closing projects. They lead teams, set goals, and ensure projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet quality standards.
Project managers also handle communication, risk management, and stakeholder engagement. Their role is crucial in coordinating efforts and guiding projects to success, making them key players in achieving organizational objectives.
Do You Need to Have A Degree to Become a Project Manager?
No, you do not need to have a degree to become a project manager. However, the path to becoming a project manager can vary significantly depending on whether you have a degree or not. Each pathway has its own set of advantages and challenges.
With a Degree
Pros:
- Structured Learning: A degree provides a comprehensive education in project management theories, methodologies, and best practices.
- Career Opportunities: Graduates may have access to higher-paying roles and more competitive positions.
- Professional Network: College or university can be a great place to build a professional network that can support your career growth.
Cons:
- Cost: Higher education can be expensive and may result in student debt.
- Time Investment: Earning a degree requires a significant time commitment, often several years.
Without a Degree
Pros:
- Flexibility: You can start gaining practical experience immediately, learning on the job.
- Lower Costs: Avoiding the financial burden of college tuition can be a major advantage.
- Alternative Education: You can pursue certifications, online courses, and workshops that are often more specific to your interests and needs.
Cons:
- Career Advancement: Climbing the career ladder might be more challenging without a degree, as some organizations prefer or require formal education.
- Skill Gaps: Self-education requires discipline, and there might be gaps in knowledge without a structured curriculum.
This guide will cover a step-by-step approach to becoming a project manager for both pathways. For those without a degree, here’s how you can start your journey:
How to Become a Project Manager Without a Degree
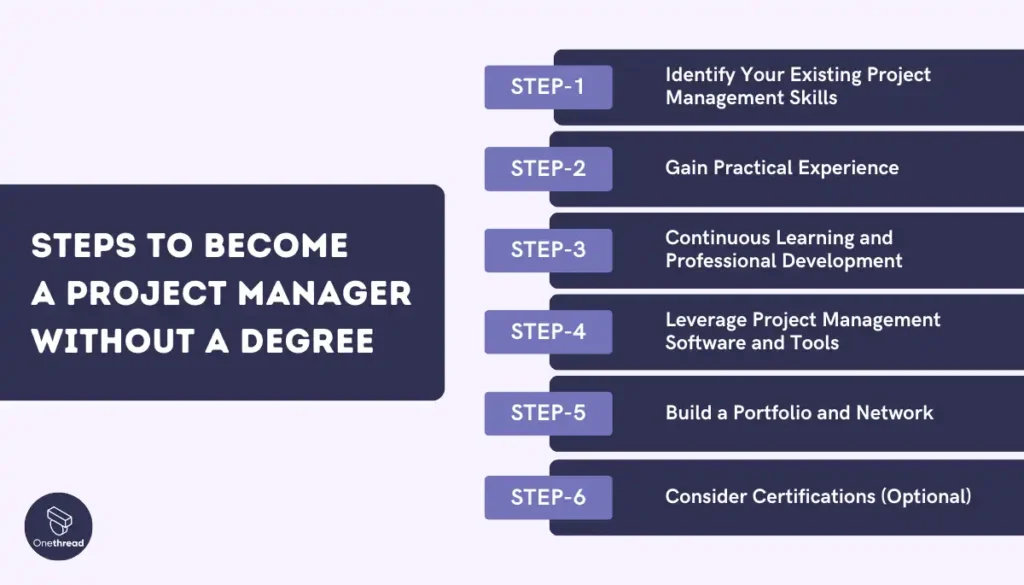
Many professionals find themselves inadvertently taking on project management responsibilities within their current roles, becoming “accidental project managers.” If this resonates with you and you’re interested in transitioning into a full-time project management career in industries like IT, tech, construction, or healthcare, here’s how you can do it without a formal degree or certification:
Step 1: Identify Your Existing Project Management Skills
Begin by assessing the project management knowledge areas you’ve already gained exposure to through your work experience in your respective industry.
This encompasses managing integration, scope, schedule, costs, quality, resources, risks, communications, procurement, and stakeholders.
For instance, in construction, you may have experience with scheduling, risk management, and contract administration. In healthcare, you might be familiar with stakeholder management and compliance requirements.
Reflect on recent projects you’ve been involved in and pinpoint the areas where you’ve contributed. This self-evaluation will help you understand your strengths and identify the gaps you need to fill.
Step 2: Gain Practical Experience
The best way to develop your project management skills is through hands-on experience. Actively seek out opportunities to take on more project-related responsibilities within your current role or organization. Volunteer for projects, even if they’re outside your typical scope of work.
This practical experience will allow you to hone your organization, scheduling, resource allocation, budgeting, risk management, and stakeholder management abilities. Don’t be afraid to learn from your mistakes – they’re valuable lessons in your journey to becoming a successful PM.
Step 3: Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Supplement your practical experience with theoretical knowledge by exploring online courses, industry-specific webinars, and networking events.
For example, IT professionals can explore courses on Agile methodologies, while those in healthcare can attend seminars on healthcare regulations and electronic health record systems.
Look into project management courses available through platforms such as Udemy, Coursera, or edX. These programs can offer a strong base in PM fundamentals, techniques, and proven practices.
Additionally, stay up-to-date with the latest trends, techniques, and tools in project management. Seek out mentorship opportunities from experienced project managers who can guide you and share their insights.
Step 4: Leverage Project Management Software and Tools
Familiarize yourself with popular project management software and tools, as they can significantly enhance your efficiency and productivity.
In construction, tools like Primavera or Procore can be invaluable. In IT and tech, proficiency in Jira or Azure DevOps can be beneficial. Healthcare professionals may find tools like HealthStream or Practice Fusion useful.
When it comes to familiarizing yourself with popular PM software and tools, Onethread stands out as a compelling option.
Designed specifically for startups, small businesses, and agile teams, Onethread offers a comprehensive suite of features to streamline project planning, execution, and monitoring.
With intuitive task management, Gantt charts, resource allocation tools, and time-tracking capabilities, Onethread empowers aspiring project managers to enhance their efficiency and productivity from the outset.
By leveraging this platform, you can not only master industry-standard project management methodologies but also demonstrate proficiency with cutting-edge technologies to potential employers.
Try Onethread
Experience Onethread full potential, with all its features unlocked. Sign up now to start your 14-day free trial!
Step 5: Build a Portfolio and Network
Document your project management experiences, successes, and lessons learned, tailoring your portfolio to showcase your industry-specific expertise. Include details about the projects you’ve worked on, the challenges you faced, and the strategies you employed to overcome them.
Participate in online project management communities and forums to connect with other professionals, share knowledge, and stay informed about job opportunities. Leverage your network to find mentors, seek advice, and potentially secure PM roles.
Step 6: Consider Certifications (Optional)
While not mandatory, obtaining a project management certification can validate your skills and knowledge, making you a more attractive candidate to employers. Popular certifications include the Project Management Professional (PMP) from the Project Management Institute (PMI), PRINCE2, Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM), and Agile certifications like Certified ScrumMaster.
For example, in construction, the Certified Construction Manager (CCM) or Certified Professional Constructor (CPC) certifications can be valuable. In healthcare, the Certified Healthcare Project Management (CHPM) certification can enhance your credibility.
Evaluate your career goals, industry preferences, and the certifications most valued in your region or sector to determine if pursuing a certification is the right path for you.
Continuously Improve and Adapt Project management is a dynamic field that constantly evolves with new methodologies, tools, and best practices. Embrace a growth mindset and commit to ongoing learning and professional development. Stay up-to-date with industry trends, attend training sessions, and seek feedback from colleagues and mentors to refine your skills continuously.
By following these steps and tailoring your efforts to your desired industry, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the path to becoming a successful project manager in IT, tech, construction, healthcare, or any other sector, even without a formal degree.
How to Become a Certified Project Manager [With Degree]
![How to Become a Certified Project Manager [With Degree]](https://www.onethreadapp.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Steps-to-Become-a-Certified-Project-Manager-1024x585.webp)
Project management offers various industries with distinct challenges and opportunities. Construction, IT, tech, and healthcare stand out as attractive industries for aspiring project managers. These industries are dynamic, have a high demand for skilled project managers, and offer rewarding careers.
Project management principles remain consistent across industries, but each sector needs a specialized approach. This guide focuses on four industries, offering a roadmap for aspiring PM.
The guide’s principles and strategies can be applied to other industries as well. Regardless of your chosen industry, the key to success lies in acquiring the right combination of education, certifications, practical experience, and a commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide that covers the path to becoming a project manager across various industries, including construction, IT, tech, and healthcare:
Step 1: Start with Self-Assessment
Begin your journey to becoming a Project Manager with a self-assessment. Evaluate your current skills, interests, and experiences to understand how they align with project management roles.
Starting with a self-assessment is crucial for aspiring Project Managers. This initial step involves taking a close look at your existing skills, both hard and soft, and determining how they align with the requirements of a project management role.
Consider your problem-solving abilities, leadership qualities, organizational skills, and any previous experience in managing projects or teams. Understanding your strengths and areas for improvement will guide you in tailoring your education, skill development, and experiences toward becoming an effective Project Manager.
This self-awareness is the foundation upon which you can build a successful career in project management.
Step 2: Earn a Relevant Bachelor’s Degree
Pursue a bachelor’s degree that aligns with your desired industry. These programs will provide you with a solid foundation in industry principles, project management methodologies, and relevant software tools.
- Construction: Bachelor’s degree in Construction Management, Civil Engineering, or a related field.
- IT/Tech: Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or a related technical field.
- Healthcare: Bachelor’s degree in Healthcare Administration, Nursing, or a related field.
Step 3: Develop Industry-Specific Technical Skills
Acquire the necessary technical skills and knowledge specific to your target industry. These skills will enable you to understand the industry’s unique challenges, processes, and best practices.
- Construction: Cost estimating, scheduling, risk management, contract administration, and safety regulations.
- IT/Tech: Programming languages, software development methodologies, database management, system analysis, and design.
- Healthcare: Healthcare regulations, standards, compliance requirements, electronic health record systems.
Step 4: Gain Relevant Work Experience
Start your career in entry-level positions within your desired industry. This hands-on experience will help you develop practical skills, understand the industry’s project life cycle, and gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and best practices.
- Construction: Entry-level positions such as assistant project manager, construction coordinator, or site engineer.
- IT/Tech: Entry-level positions such as software developer, systems analyst, or IT support specialist.
- Healthcare: Entry-level positions such as medical assistant, nurse, or healthcare administrator.
Step 5: Obtain Professional Project Management Certifications
Demonstrate your project management expertise and commitment to the profession by obtaining relevant certifications. These certifications are widely recognized and can enhance your credibility and career opportunities.
- Common Certifications: Project Management Professional (PMP), Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)
- Industry-Specific Certifications:
- Construction: Certified Construction Manager (CCM), Certified Professional Constructor (CPC)
- IT/Tech: Certified ScrumMaster (CSM)
- Healthcare: Certified Healthcare Project Management (CHPM)
Step 6: Build Project Management Skills
Actively seek opportunities to work on projects within your respective industry, either as a team member or project coordinator. This hands-on experience will allow you to develop essential project management skills tailored to your industry’s unique challenges and best practices.
Develop skills in project planning, risk management, resource allocation, stakeholder management, and communication.
Step 7: Develop Soft Skills
Effective project management requires a combination of technical and soft skills. Focus on developing essential soft skills that are crucial for successful project delivery and team management.
- Communication skills
- Leadership skills
- Problem-solving skills
- Conflict resolution
- Negotiation
Step 8: Pursue Continuing Education
Stay current with emerging trends, technologies, and best practices in your industry by participating in continuing education programs. This will ensure that your knowledge and skills remain up-to-date and relevant.
- Attend industry-specific conferences, seminars, and workshops.
- Participate in online courses and certifications to enhance your expertise.
Step 9: Gain Experience in Project Management Roles
As you progress in your career, actively seek out project management roles with increasing levels of responsibility within your industry. This hands-on experience will help you build a solid track record of successfully delivering projects on time, within budget, and meeting stakeholder requirements.
Step 10: Consider Advanced Degrees (Optional)
Depending on your career goals and industry, you may consider pursuing a Master’s degree in Project Management, Business Administration, or a related field. Advanced degrees can enhance your credentials, deepen your knowledge, and open up additional career advancement opportunities.
Step 11: Continuously Develop Your Skills
Successful project managers continuously strive to improve their skills and stay up-to-date with industry developments. Engage in ongoing professional development activities to maintain your competitive edge.
- Stay updated with industry-specific regulations, technologies, and methodologies through continuous learning.
- Maintain your professional certifications by completing the required continuing education credits.
- Network with other project management professionals and join industry associations to expand your knowledge and connections.
By following this comprehensive guide and tailoring your efforts based on your desired industry, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the path to becoming a successful project manager in construction, IT, tech, healthcare, or any other industry of your choice.
As you set out on your journey to become a project manager, it’s essential to understand the specific requirements and potential career paths within your chosen industry. To assist you further, we’ve compiled a comprehensive table that outlines the formal education, professional certifications, and salary ranges for various industries, including construction, IT, tech, healthcare, and many others.
Industries for Project Managers | Required Formal Education | Desired Professional Certification | Annual salary Range |
Architecture | Bachelor's degree in Architecture or related field | Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM), LEED Accredited Professional | $65,000 - $120,000 |
Oil and Gas | Bachelor's degree in Engineering, Business Administration, or related field | PMP, Project Management for the Oil and Gas Professional (PM-OGP), Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) | $80,000 - $150,000 |
Biotech | Bachelor's degree in Biology, Biotechnology, or related field. Master's or Ph.D. preferred | PMP, Certified Professional in Bio pharmaceutical Project Management (CPBPM) | $75,000 - $135,000 |
Healthcare | Bachelor's degree in Healthcare Administration, Nursing, or related field. Master's degree preferred | Project Management Professional (PMP), Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM), Certified Healthcare Project Management (CHPM) | $70,000 - $135,00 |
Construction | Bachelor's degree in Civil Engineering, Construction Management, or related field | PMP, Certified Construction Manager (CCM), Certified Professional Constructor (CPC) | $70,000 - $130,000 |
Civil Engineering | Bachelor's degree in Civil Engineering | PMP, Professional Engineer (PE) license | $70,000 - $125,000 |
Clinical Research | Bachelor's degree in Life Sciences, Nursing, or related field. Master's or Ph.D. preferred | PMP, Certified Clinical Research Professional (CCRP) | $75,000 - $140,000 |
Real Estate | Bachelor's degree in Business Administration, Real Estate, or related field | PMP, Certified Commercial Investment Member (CCIM) | $65,000 - $120,000 |
Information Technology (IT) | Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Information Systems, or related field | PMP, Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM), Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) | $75,000 - $140,000 |
Pharmaceutical Industry | Bachelor's degree in Life Sciences, Pharmacy, or related field. Master's or Ph.D. preferred | PMP, Certified Professional in Bio pharmaceutical Project Management (CPBPM) | $80,000 - $150,000 |
Technology | Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or related field | PMP, Certified ScrumMaster (CSM), Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) | $80,000 - $145,000 |
[Note that the salary ranges provided are approximate and can vary based on factors such as location, company size, and individual experience.]
Whether you’re just starting to explore project management careers or are seeking to transition into a new industry, this table offers a clear roadmap to help you navigate the diverse array of opportunities available.
Roles of a Project Manager
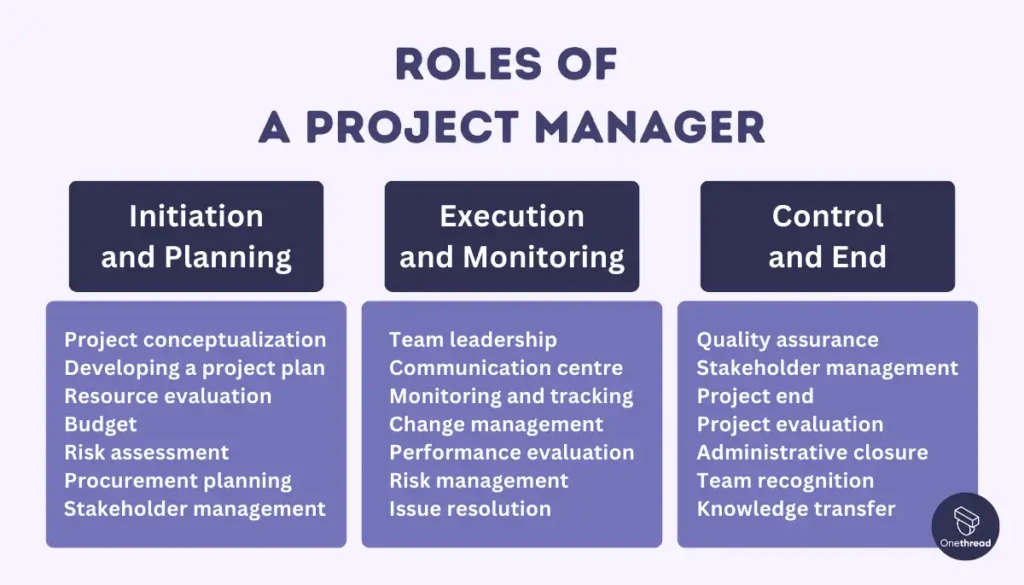
Project managers play a pivotal role in leading projects from conception through completion, ensuring that they meet objectives within the stipulated time and budget constraints. Here’s a more comprehensive look at their roles across various project phases:
Initiation and Planning
The beginning and planning stages are when the project is conceptually formed. Project managers lead, execute, or assist with several areas during these phases:
- Project conceptualization: Setting the project’s objectives, boundaries, and outputs, and achieving consensus among stakeholders.
- Developing a project plan: Crafting a comprehensive schedule that specifies tasks, interdependencies, key milestones, and the overall project timeline.
- Resource evaluation: Determining the needs for resources and confirming that the team possesses the appropriate tools, expertise, and staff for successful completion.
- Budget: Establishing and managing the budget of a project, including cost estimations, forecasting, and control measures.
- Risk assessment: Identifying potential risks and developing risk management strategies to mitigate or eliminate them.
- Procurement planning: Determining the need for external resources, such as vendors or contractors, and managing the procurement process.
- Stakeholder management: Identifying and engaging stakeholders, managing expectations, and ensuring effective communication throughout the project.
Execution and Monitoring
During the execution phase, the project manager oversees the team’s progress and ensures adherence to the project plan.
- Team leadership: Motivating and guiding team members, fostering collaboration, resolving conflicts, and providing necessary support.
- Communication centre: Serving as the primary communication hub, updating stakeholders on advancements, challenges, and critical choices.
- Monitoring and tracking: Monitoring essential performance metrics, evaluating data, and making necessary adjustments to keep the project aligned with its goals.
- Change management: Effectively managing and controlling changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget, while minimizing disruptions.
- Performance evaluation: Monitoring team performance, providing feedback, and addressing any performance issues or training needs.
- Risk management: Proactively identifying new and ongoing risks, implementing contingency plans, and mitigating risks to minimize disruptions.
- Issue resolution: Tackling roadblocks and challenges that cannot be resolved by the team members, and finding solutions to keep the project on track.
Control and End
During the control and end phases, project managers ensure quality assurance, manage stakeholder expectations, and facilitate project end activities.
- Quality assurance: Applying quality assurance practices to confirm that deliverables satisfy client expectations and comply with set standards.
- Stakeholder management: Handling stakeholder expectations, resolving their issues, and guaranteeing their contentment with the project’s results.
- Project end: Completing the project by finalizing deliverables, transferring ownership, and obtaining formal acceptance from stakeholders.
- Project evaluation: Facilitating postmortem of a project or lessons learned session, evaluating what worked well, identifying areas for improvement, and capturing insights for future projects.
- Administrative closure: Ensuring all project documentation is complete, accurate, and properly archived for future reference.
- Team recognition: Acknowledging and celebrating the team’s achievements, contributions, and successful project completion.
- Knowledge transfer: Facilitating the transfer of project knowledge and lessons learned to relevant parties within the organization.
Project managers play a crucial role throughout the project lifecycle, orchestrating resources, managing stakeholders, mitigating risks, and ensuring successful project delivery. Their responsibilities span planning, execution, control, and closure, requiring strong leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills.
Essential skills for PM
Project Managers need a mix of hard and soft skills to successfully lead projects. Hard skills include project planning, risk management, and budgeting. Soft skills encompass leadership, communication, and problem-solving abilities, ensuring effective team management and stakeholder engagement.
Hard Skill

Project managers need strong hard skills like-
Project Management Methodologies
Project Managers must master various PM methodologies like Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall, each offering unique frameworks for managing projects. Agile focuses on flexibility and continuous improvement, Scrum facilitates quick iterations, and Waterfall emphasizes linear progression.
- Agile: Agile project management supports adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continual improvement. It encourages rapid and flexible response to change, making it suitable for projects with evolving requirements.
- Scrum: A subset of Agile, Scrum is used for managing complex projects through short sprints, allowing teams to adjust quickly to changing project requirements. It involves regular stand-ups and sprint reviews to ensure team alignment and progress.
- Waterfall: This traditional project management methodology follows a sequential, linear process. Each phase must be completed before the next begins, making it ideal for projects with well-defined requirements and no expected changes.
Knowing these methodologies enables Project Managers to choose the best approach based on the project’s nature, ensuring efficient execution and successful delivery.
Budgeting And Cost Analysis
Budgeting and cost analysis are crucial for Project Managers to estimate the financial resources needed, control expenses, and ensure projects stay within budget. Mastery of these skills enables effective allocation, monitoring, and adjustment of funds to meet project objectives without overspending.
Project Managers must accurately forecast the total costs of projects, including direct and indirect expenses, to develop a comprehensive budget. This involves analyzing various cost factors such as labor, materials, equipment, and overheads.
Effective budgeting ensures that all financial resources are allocated wisely, while cost analysis helps in identifying areas where expenses can be reduced or where additional investment is needed.
Regular monitoring and revising of the budget are essential to address any financial discrepancies early, ensuring the project’s financial health and success.
Risk Assessment And Mitigation
Risk assessment and mitigation are critical for identifying potential project obstacles and developing strategies to avoid or minimize their impact. Project Managers must evaluate risks for likelihood and consequence, prioritizing actions to protect the project’s success.
Effective risk management involves identifying potential risks, analyzing their possible impact on the project, and prioritizing them based on their severity.
Project Managers then develop and implement strategies to mitigate these risks, such as contingency planning, risk avoidance, transfer, or acceptance.
This proactive approach ensures that risks are managed and controlled efficiently, minimizing disruptions and keeping the project on track toward its objectives.
Scheduling and Timeline Management
Project Managers must create realistic project schedules that outline all tasks, their durations, dependencies, and deadlines.
Effective timeline management involves continuously monitoring progress against the plan, adjusting schedules as needed to accommodate changes or delays, and ensuring that project milestones are met on time.
This requires a deep understanding of the project scope, resources available, and potential bottlenecks.
Proficiency in Project Management Software
Familiarity with project management tools such as Onethrwad, Asana, Trello, and Monday.com is crucial for modern Project Managers. These platforms facilitate project planning, task assignment, progress tracking, and collaboration among team members.
Proficiency in these tools enables Project Managers to maintain an organized overview of all project aspects, enhance team communication, and streamline workflow processes. Mastery of project management software is a key enabler for delivering projects efficiently and effectively.
Proficiency in project management software is a key enabler for delivering projects efficiently and effectively, and Onethread emerges as a powerful tool in this regard.
Designed with a user-friendly interface and optimized for small businesses and agile teams, Onethread facilitates seamless project planning, task assignment, progress tracking, and team collaboration.
Its visual task boards, calendar views, and robust reporting features provide an organized overview of all project aspects, enabling aspiring project managers to maintain a clear understanding of timelines, dependencies, and potential bottlenecks.
By mastering Onethread, you can enhance your ability to communicate effectively with stakeholders, streamline workflow processes, and ultimately, drive successful project outcomes.
Try Onethread
Experience Onethread full potential, with all its features unlocked. Sign up now to start your 14-day free trial!
Soft Skills
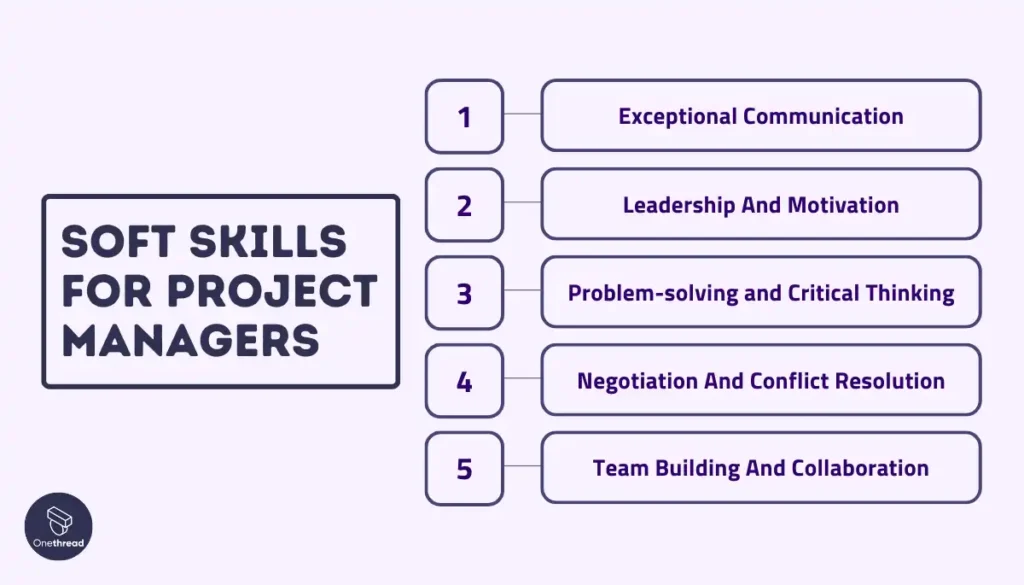
Exceptional communication, leadership, problem-solving, negotiation, and team building are pivotal soft skills for PM. These competencies facilitate effective team guidance, issue resolution, and stakeholder engagement, ensuring project success.
Exceptional Communication
Exceptional communication, both written and verbal, is a soft skill crucial for Project Managers to convey project goals, updates, and feedback clearly and effectively. This skill ensures all stakeholders are aligned and informed throughout the project lifecycle.
Project Managers must articulate project objectives, expectations, and changes in a way that is accessible to everyone involved, from team members to stakeholders. Effective communication involves not just the transmission of information but also ensuring comprehension and engagement.
This includes writing clear reports and emails, giving compelling presentations, and facilitating productive meetings. Mastery of this skill is essential for maintaining project transparency, fostering collaboration, and ensuring project success.
Leadership And Motivation
Leadership and motivation are vital soft skills for PM, enabling them to inspire and guide their teams toward achieving project goals. Effective leadership fosters a positive environment and motivates team members to contribute their best.
A Project Manager’s ability to lead involves setting a clear vision, encouraging teamwork, and maintaining high morale.
By demonstrating confidence, empathy, and decisiveness, they motivate individuals to excel, ensuring the project’s success through collaborative effort and a shared sense of purpose.
Problem-solving and Critical Thinking
Problem-solving and critical thinking are indispensable soft skills for PM, allowing them to navigate through challenges and obstacles that arise during a project’s lifecycle.
This skill set is crucial for analyzing complex situations, identifying underlying problems, and evaluating potential solutions.
By applying critical thinking, Project Managers can weigh the pros and cons of different approaches and choose the most effective strategy for moving forward. This ensures that projects stay on track, meet their objectives, and overcome any hurdles efficiently.
Negotiation And Conflict Resolution
Negotiation and conflict resolution skills are also vital for Project Managers, as they often find themselves mediating between different stakeholders, team members, and clients.
The ability to negotiate effectively and resolve conflicts is key to maintaining harmony within the team and ensuring stakeholder satisfaction.
By understanding different perspectives and finding common ground, Project Managers can defuse tensions and foster a collaborative environment. This not only keeps the project moving forward but also strengthens relationships and builds trust among project participants.
Team Building And Collaboration
Team building and collaboration are equally important, as the success of a project often hinges on the ability of the team to work together effectively. Project Managers must be adept at bringing individuals together, creating a sense of unity, and encouraging collaboration.
This involves establishing clear communication channels, promoting mutual respect, and leveraging the diverse skills and perspectives of team members.
By fostering an environment that values teamwork and collaboration, Project Managers can enhance productivity, spur innovation, and ensure that the project achieves its goals in a cohesive and integrated manner.
Job Outlook For Project Managers
projects that employers will need to fill 2.3 million new project-oriented roles annually through 2030. This demand is fueled by the continuous need for organizations to improve efficiency, implement new technologies, and drive strategic initiatives, making project management skills increasingly valuable across industries.
As for salaries, project manager compensation varies widely depending on the industry, location, and experience level. In the United States, the average annual salary for a project manager ranges from approximately $75,000 to $135,000.
Entry-level project managers can expect salaries on the lower end of this range, while experienced professionals in high-demand sectors or with specialized skills can command salaries at or above the upper limit. This range reflects the diverse opportunities and financial rewards available in the project management profession, highlighting its appeal as a career path.
FAQs
Do I need a degree to become a project manager?
A degree is highly beneficial but not mandatory. Relevant experience, certifications, and skills can also lead to project management roles.
Is it possible to become a project manager without experience?
Yes, it’s possible by starting in entry-level positions, gaining relevant skills, and leveraging certifications to demonstrate your knowledge and competency in project management.
What qualifies you to be a project manager?
Qualifications include a mix of education, experience, and skills in leadership, organization, communication, and problem-solving. Certifications like PMP or PRINCE2 can also significantly enhance your qualifications.
How can I start my career as a project manager?
Begin by gaining experience in project-oriented roles, educate yourself on project management principles, and seek mentorship. Pursue certifications and build skills in leadership, planning, and risk management.
How long does it take to become a project manager?
It varies but typically requires several years. Gaining relevant experience through roles in project teams and acquiring project management education or certifications can take anywhere from 2 to 5 years.
Conclusion
Embarking on a project management career is a journey of continuous learning, experience-building, and skill enhancement. Whether through formal education or self-driven paths, success as a project manager demands dedication, adaptability, and a passion for leading teams to achieve goals. With the growing demand for skilled project managers across industries, there’s never been a better time to start shaping your future in this dynamic field.
