In the realm of project management, one indispensable tool stands tall as a guiding beacon for successful project execution – the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). With its hierarchical framework, the WBS offers a comprehensive roadmap that meticulously dissects complex projects into manageable tasks, activities, and deliverables.
This structured approach empowers project teams to better comprehend the project’s scope, allocate resources efficiently, and communicate effectively with stakeholders.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Work Breakdown Structure, exploring its significance in project planning, execution, and control. Through a semi-formal lens, we will examine how this fundamental tool streamlines workflows, enhances collaboration, and mitigates potential risks. Join us as we unravel the importance of the WBS and its pivotal role in steering projects toward successful outcomes.
What Is A Work Breakdown Structure?
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical project management process that breaks down a complex project into smaller, manageable components.
It provides a visual and organized representation of the project’s scope, deliverables, activities, and tasks, allowing project teams to better understand and plan the work required to achieve the project’s objectives.
At its core, a WBS is structured in a tree-like format, with the top level representing the overall project, and subsequent levels breaking it down into more detailed elements.
Each level of the WBS further dissects the project into smaller work packages, making it easier to assign responsibilities, estimate resources, and track progress.
The WBS plays a crucial role in project planning and execution as it enables effective communication among team members and stakeholders. By providing a clear and comprehensive breakdown of the project’s components, it enhances collaboration, facilitates resource allocation, and aids in identifying potential risks and dependencies.
In essence, a Work Breakdown Structure is an essential tool that guides project managers and teams in successfully organizing and managing projects of varying complexities.
Why Use a Breakdown Structure In Project Management?

Using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in project management offers several significant advantages that contribute to the successful planning, execution, and control of projects. Here are some key reasons why a WBS is essential:
Clarity and Understanding
The WBS provides a clear and organized representation of the project’s scope, objectives, and deliverables. It breaks down the complex project into smaller, manageable components, making it easier for project teams to understand their roles and responsibilities.
Effective Planning
By dividing the project into smaller work packages and activities, the WBS enables efficient project planning. It allows project managers to estimate resource requirements, set realistic timelines, and allocate tasks to the right team members.
Resource Allocation
With a detailed WBS in place, project managers can precisely allocate resources to each work package. This ensures that resources, such as manpower, budget, and equipment, are used optimally, minimizing waste and delays.
Communication and Collaboration
The WBS serves as a common reference point for all project stakeholders. It enhances communication by providing a shared understanding of the project’s structure and progress, facilitating better collaboration among team members, clients, and other stakeholders.
Control, Schedule, and Tracking
The hierarchical nature of the WBS allows for effective project control and tracking. Project managers can monitor progress at different levels, identify bottlenecks, and address potential issues before they escalate.
Risk Identification and Mitigation
With a detailed breakdown of the project, potential risks and dependencies become more apparent. The WBS helps in identifying critical paths and areas that might be prone to risks, enabling proactive risk management.
Scope Management
The WBS acts as a baseline for scope management. Any changes or additions to the project scope can be easily integrated into the existing structure, ensuring that all aspects of the project are accounted for and managed effectively.
Scalability
The WBS can be adapted to suit projects of varying sizes and complexities. It is equally useful for small, straightforward projects as well as large, multifaceted endeavors.
In summary, a Work Breakdown Structure is an indispensable tool in project management, promoting efficiency, collaboration, and control throughout the project lifecycle. It empowers project teams to navigate complexities, meet objectives, and deliver successful outcomes in a systematic and organized manner.
How To Create A Work Breakdown Structure?
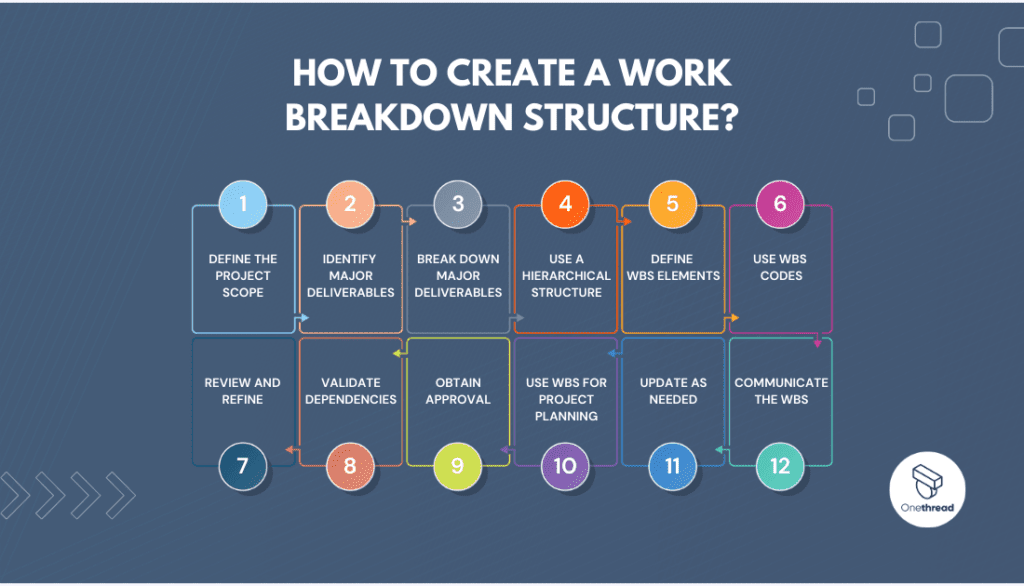
Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) involves a step-by-step process that helps break down a project into smaller, manageable tasks and deliverables. Here’s a guide on how to create a WBS:
Define the Project Scope
Clearly outline the project’s objectives, deliverables, and overall scope. Understand the project’s requirements and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned on the project’s goals.
Identify Major Deliverables
List down the major deliverables or outcomes that need to be achieved to fulfill the project’s objectives. These are the top-level elements of your WBS.
Break Down Major Deliverables
For each major deliverable, further decompose them into smaller, more specific tasks or work packages. Keep breaking down the elements until they represent manageable work units that can be easily estimated and assigned.
Use a Hierarchical Structure
Organize the WBS in a hierarchical format, with the major deliverables at the highest level (Level 1), sub-deliverables or work packages at the subsequent levels (Level 2, Level 3, and so on).
Define WBS Elements
Assign clear and concise names to each element of the WBS to ensure understanding and avoid ambiguity. Use action-oriented verbs to describe the tasks.
Use WBS Codes
Assign unique identifiers or codes to each WBS element. These codes help in tracking and referencing different elements of the WBS.
Review and Refine
Continuously review and refine the WBS with input from stakeholders and subject matter experts. Ensure that all project components are accounted for and that the WBS represents a comprehensive breakdown of the project.
Validate Dependencies
Identify any dependencies between different tasks or work packages within the WBS. Understanding these dependencies will help in creating an accurate project schedule.
Obtain Approval
Once the WBS is complete, seek approval from key stakeholders, including the project sponsor and project team members, to ensure everyone is in agreement with the breakdown.
Use WBS for Project Planning
Utilize the WBS as a foundation for project planning, resource allocation, and scheduling. The WBS will serve as a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Update as Needed
As the project progresses, update the WBS to reflect any changes, additions, or modifications to the scope or tasks.
Communicate the WBS
Share the WBS with all project stakeholders to ensure everyone involved has a clear understanding of the project’s structure and the tasks they are responsible for.
Remember that the level of detail in the WBS should be tailored to the specific project’s size, complexity, and requirements. A well-structured WBS lays the groundwork for effective project management and successful project delivery.
Levels Of A Work Breakdown Structure
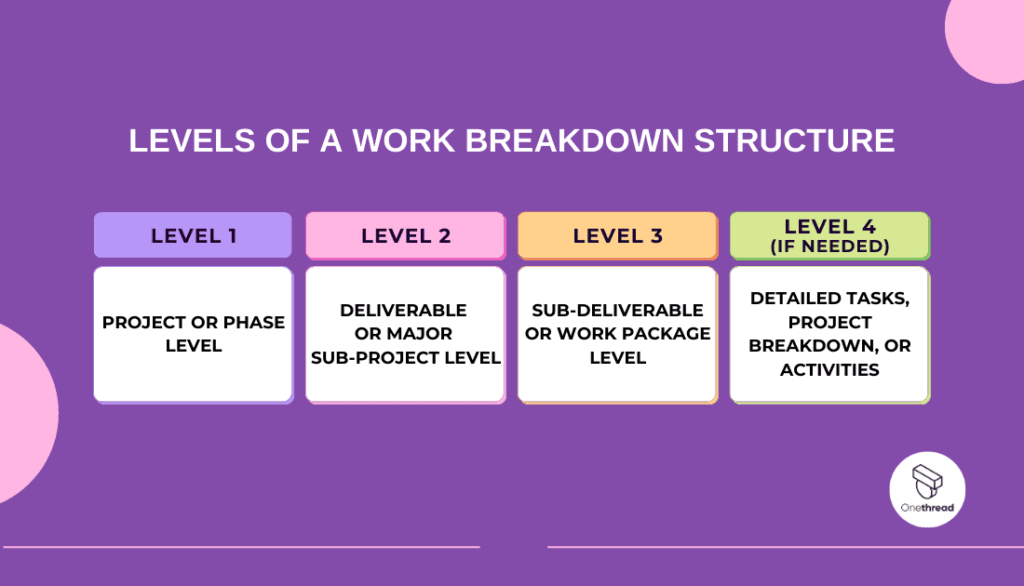
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) typically consists of multiple levels that represent a hierarchical breakdown of a project into increasingly detailed components. The number of levels in a WBS can vary depending on the size, complexity, and requirements of the project. However, a standard WBS usually contains three to four levels. Here’s a brief explanation of each level:
Level 1: Project or Phase Level
- This is the top-level of the WBS and represents the entire project or major phases if the project is divided into distinct phases.
- Level 1 elements are the most significant deliverables or outcomes of the project, providing a high-level overview of what needs to be achieved.
- Examples of Level 1 elements could include “Project Initiation,” “Design Phase,” “Development Phase,” “Testing Phase,” and “Project Closure.”
Level 2: Deliverable or Major Sub-Project Level
- Level 2 breaks down the Level 1 elements into more manageable components, representing the major deliverables or sub-projects within each phase.
- It further elaborates on the Level 1 elements, providing a more detailed breakdown of the project’s scope.
- Examples of Level 2 elements could be “Requirements Gathering” and “Prototyping” under the “Design Phase” or “User Acceptance Testing” under the “Testing Phase.”
Level 3: Sub-Deliverable or Work Package Level
- At Level 3, the deliverables from Level 2 are further broken down into smaller, concrete work packages or tasks.
- Level 3 elements represent the specific activities or components that need to be completed to accomplish the Level 2 deliverables.
- Examples of Level 3 elements could include “Conduct Stakeholder Interviews” or “Create Wireframes” under the “Requirements Gathering” deliverable.
Level 4 (if needed): Detailed Tasks, Project Breakdown, or Activities
- In some cases, a WBS may have a Level 4, which breaks down the Level 3 work packages into even more detailed tasks or activities.
- This level is optional and is used when the project requires a more granular breakdown of the work.
- Examples of Level 4 elements could include “Contact Stakeholders for Interview Scheduling” or “Revise Wireframes Based on Feedback.”
It’s important to note that the number of levels in a WBS may vary based on the complexity of the project and the level of detail needed for effective planning and management. The WBS should strike a balance between providing enough detail for clarity and control while avoiding unnecessary complexity.
WBS in Project Management
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a fundamental tool in project management that helps to organize and define the scope of a project. It is a hierarchical representation of the project’s tasks, activities, and deliverables, broken down into smaller and more manageable components.
The WBS serves as a visual map that helps project managers and teams understand the project’s structure, dependencies, and the overall scope of work. Here’s how the WBS is used in project management:
Scope Definition
The primary purpose of a WBS is to define the scope of a project. It breaks down the project’s main objectives into smaller, more manageable tasks and deliverables. This ensures that all aspects of the project are captured and that nothing important is overlooked.
Hierarchical Structure
A WBS is organized in a hierarchical manner. The top level represents the project as a whole, and each subsequent level breaks down the work into smaller and more specific components. This makes it easier to understand the relationships between different tasks and their dependencies.
Task Assignment and Responsibility
The WBS helps allocate tasks to specific team members or departments. Each task or deliverable can be assigned to responsible individuals or teams, ensuring clarity about who is accountable for each component of the project.
Estimation and Resource Allocation
By breaking down the project into smaller tasks, it becomes easier to estimate the time, effort, and resources required for each component. This aids in more accurate project planning and resource allocation.
Scheduling and Time Management
With a clear breakdown of tasks and their dependencies, project managers can create a detailed project schedule. They can identify critical paths, potential bottlenecks, and areas where adjustments are needed to meet deadlines.
Risk Management
A well-defined WBS allows project managers to identify potential risks and uncertainties associated with specific tasks. This enables proactive risk management by addressing potential issues before they escalate.
Communication
The WBS provides a visual representation of the project’s structure, which makes it easier to communicate the project’s scope and progress to stakeholders, team members, clients, and executives. It serves as a common reference point for discussions and updates.
How Onethread Helps Streamline Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Onethread is a cutting-edge project management software designed to optimize the creation and management of Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) in project planning. Its unique set of features facilitates a more efficient, transparent, and collaborative approach to breaking down complex projects into manageable components. Here’s why it helps in WBS:
Hierarchical Visualization
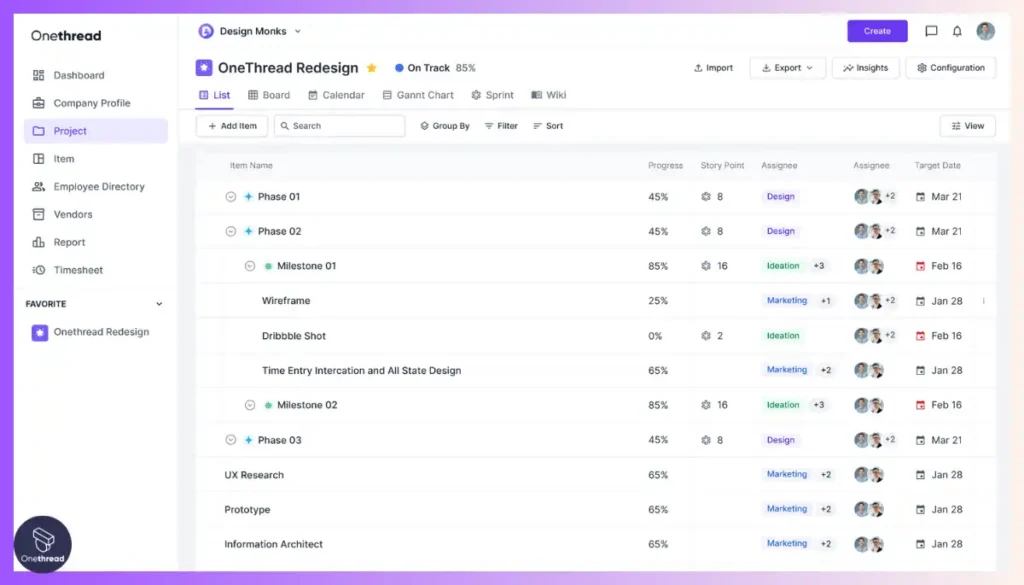
Onethread provides an intuitive hierarchical visualization of the WBS, allowing users to see the breakdown of tasks and sub-tasks in a structured manner. This enables project managers and team members to easily grasp the project’s scope and the relationships between different tasks.
Drag-and-Drop Interface
Onethread’s drag-and-drop interface simplifies the process of arranging tasks and sub-tasks within the WBS. This feature enhances usability and expedites the initial setup of the project structure.
Dependency Mapping
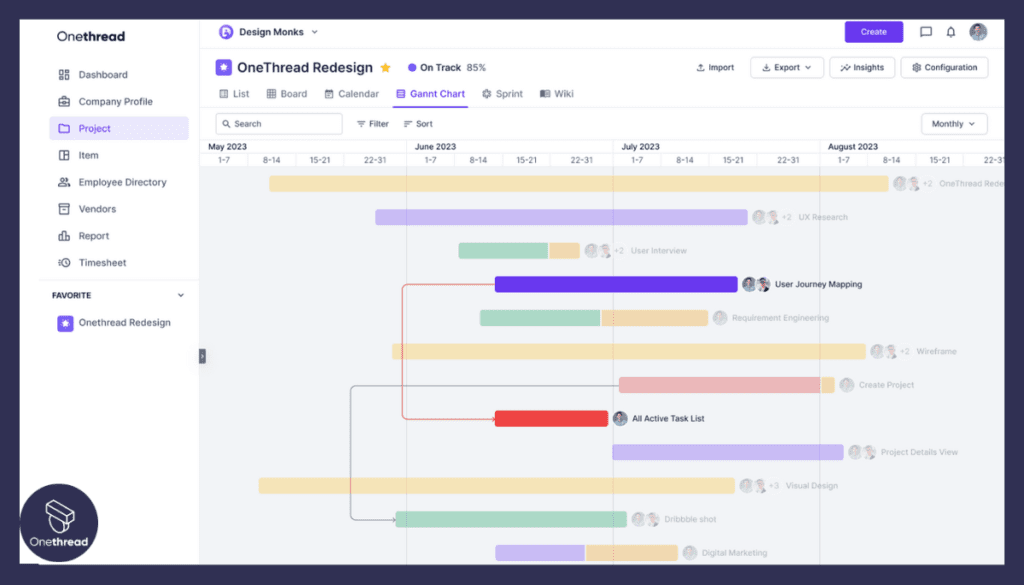
Onethread offers robust dependency mapping capabilities. Users can define task dependencies and linkages between various components of the project. This feature helps in identifying critical paths, potential bottlenecks, and areas where delays might occur.
Resource Allocation Insights
Onethread’s resource allocation feature provides insights into the availability and allocation of team members. This aids in making informed decisions about task assignment and ensures that the right resources are allocated to the right tasks.
Change Impact Analysis
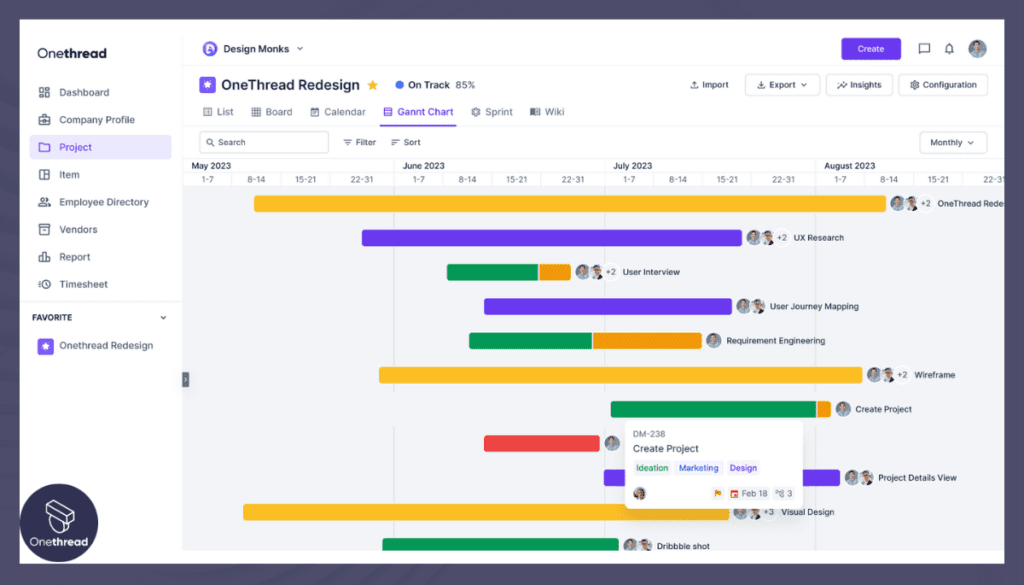
When changes occur, Onethread’s change impact analysis feature evaluates how modifications to one task affect the entire WBS. This enables better decision-making by understanding the consequences of potential changes.
Final Words
Creating and utilizing a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a critical step in effective project management. A well-structured WBS provides a clear and organized representation of a project’s scope, deliverables, and tasks, enabling teams to plan, execute, and control projects with greater efficiency and success.
Among the various software options available, Onethread stands out as a powerful tool for WBS creation. Its user-friendly interface, collaborative features, and real-time updates make it a top choice for project teams seeking streamlined project planning and execution.
However, the right software choice depends on the specific needs and preferences of each project team. By investing time and effort into creating a detailed WBS, project managers and teams can lay a strong foundation for project success and delivering high-quality results within designated timelines and budgets.
FAQs
How is a WBS different from a project schedule?
While a project schedule outlines the chronological order of tasks, a WBS focuses on breaking down the project’s scope into smaller components, showing the relationships and dependencies between tasks.
What role does a WBS play in risk management?
A WBS helps identify potential risks by highlighting dependencies and relationships between tasks. This aids in identifying critical paths, where delays or issues might impact the project timeline and outcomes.
What’s the difference between a WBS and a Gantt chart?
A WBS is a hierarchical breakdown of project tasks, while a Gantt chart is a visual representation of project tasks on a timeline. The WBS focuses on task structure, while the Gantt chart emphasizes task scheduling.
How can software tools assist in creating and managing a WBS?
Project management software tools often provide features to create, visualize, and manage WBS hierarchies. They may include drag-and-drop interfaces, real-time collaboration, dependency tracking, and reporting capabilities to enhance the WBS process.